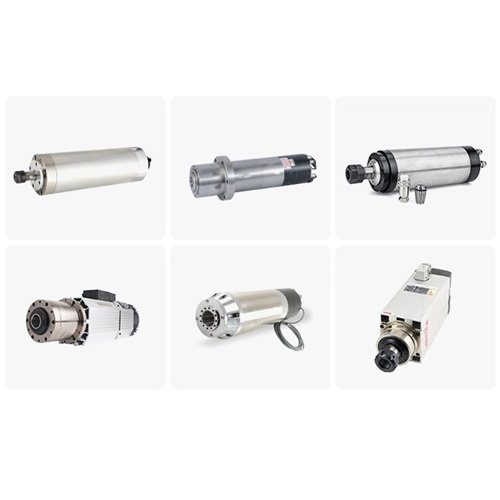
A spindle motor is an electric motor that creates high-speed rotational motion and holds the tool in a CNC machine. The high rotation speed generated by the spindle motor helps the CNC machine perform better in cutting and engraving materials. Regular motors cannot achieve such speeds in rotational motion. Another difference between a spindle motor and a regular motor is the synchronization of its rotor. Synchronization of the rotor means that if the load on the shaft changes, the motor’s rotational speed will not change. Various types of spindles can be used in a CNC machine. In the following section, we will learn about different spindle motors.

Types of Spindle Motors
CNC machine spindles come in various types. Before selecting and purchasing a spindle motor for a CNC machine, it is better to become familiar with its types. Below, we will learn about the different types of electric motors.
Water-Cooled Spindle Motor
A water-cooled spindle uses the flow of water to dissipate heat. In this electric motor, two water pipes are connected to the motor to cool it down. One of these pipes brings water to the spindle block and goes out from the other pipe. Although using a water-cooling system in a CNC machine is more efficient in cooling the spindle, it requires specific maintenance. For example, if the water pressure entering the spindle body is too high, it can lead to water seeping or pouring into the chamber, causing the system to fail. Additionally, if a foreign object blocks the water flow, the cooling system will be disrupted, and the motor may burn out in a short time.
One of the main advantages of water-cooled spindle motors over ai-cooled spindle motors is their lower noise creation. Due to using liquid for the cooling system, not only does this spindle better cool the system but it also operates in lower noise.

some experts recommend it is better to move the working table in the X and Y directions instead of moving the spindle motor in case you are using water-cooled spindle motors.
Air-Cooled Spindle Motor
An air-cooled spindle uses a fan that rotates at the same speed as the shaft to cool the motor. The spindle plays an important role in a CNC machine, so ensuring its proper functioning is essential for achieving optimal results from the machine. The advantage of an air-cooled spindle over a water-cooled spindle is that its cooling system is connected to the shaft and rotates simultaneously with it. This means that if the motor is in good condition and produces rotational motion, the fan will work; if the motor stops for any reason, the fan also stops. With this feature, the air-cooled spindle always has an operational cooling system, eliminating the worry of the motor burning out. In contrast, as mentioned above, in a water-cooled spindle, the motor might be rotating while the cooling system is disrupted, leading to motor burnout. As mentioned earlier, this spindle motor rotates at a very high speed, so its fan can make a lot of noise because the fan is also rotating at the same speed.

Difference Between Automatic Tool Change and Manual Spindles
From another perspective, spindles are divided into two categories: automatic tool change and manual. To understand the difference between these two categories, we need to learn more about how a spindle operates in a CNC machine. We know that one of the spindle’s tasks is to produce high-speed rotational motion. Another task of the spindle motor is to hold the working tool. The working tool is the piece that is placed between the spindle and the object to be machined. For working on different parts of an object, different tool diameters and types may be required. Changing these tools manually can lead to wasted time. The difference between tool change and manual spindles becomes clear here. Tool change spindles can automatically perform tool changes without operator intervention, while in manual spindles, the operator must remove the tool from the spindle and replace it with a new one. Also, after changing the tool, the operator needs to set the tool up and calibrate it. Tool change spindles are suitable for machines that need to change tools multiple times during the operation.

Application of Collets in Spindles
There are two main types of holding tools via spindle motors. In both methods, we need an intermediary product called Collet Chuck to hold the working tool and connect it to the spindle motor. The connection between collet chunk and spindle has two types. First, the spindle has a rotational shaft outside and is installed on it. Second, the spindle has a hole instead of a shaft, and a collet with cone shape in installed in the hole.
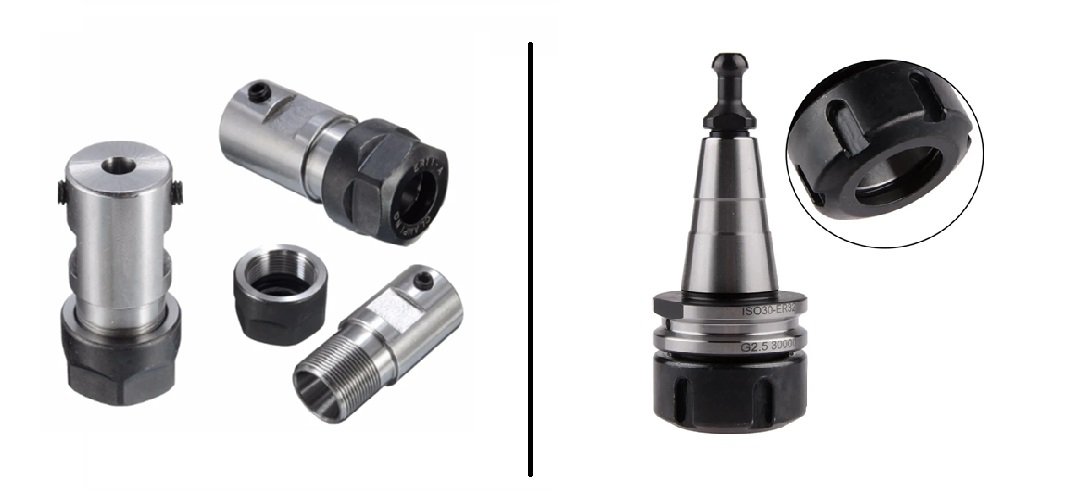

In automatic tool change spindles, cone holders are usually used. The visible difference between these chunks is that the collet connects to a shaft extending from the spindle and holds the tool; whereas in spindles using cone chunks, no shaft extends from the spindle, and the collet chuck fits into the spindle.
These collet chunks consist of three parts: the body, the nut, and the collet itself.